
Hot packs are often very therapeutic and allow gentle mobilisation by the physiotherapist. The goals of rehabilitation are to relieve stiffness, restore range of motion and increase muscle strength. As with any joint reconstruction, the outcome is very much dependent upon the surgeon’s skill in realigning the normal joint anatomy.įollowing surgery, rehabilitation can be resumed once the surgeon has given the go ahead and removed any plaster casting. This has the advantage of not requiring a plaster cast, so rehabilitation with a chartered physiotherapist can commence much earlier.Įven following surgery there is a reasonably high risk of long term arthritis of the CMC joint of the thumb. In these circumstances the surgeon has to make an incision and uses a small screw to re-attach the bony fragments. However, the level of stability attained is limited and the surgical wire is not appropriate where the fracture fragments are not well aligned. The first is less invasive and involves inserting a surgical wire through the fracture site without making an incision. There are two main surgical methods for a Bennett’s fracture. However, because of the long term problems and functional instability that can occur, many orthopaedic doctors advocate surgical fixation to repair a Bennett’s fracture dislocation. Use a bone healing system to speed up broken bone healingīecause of the combination of damage to the joint surface of the metacarpal at the CMC joint, and the joint instability caused by the detachment of the deep ulnar ligament, the incidence of long term degenerative joint disease (arthritis) in the CMC joint is high following a Bennett’s fracture.Īlso, Bennett’s fractures that are managed conservatively tend to experience a fair degree of functional impairment, such as re-dislocation and subluxation during work and sporting activities, although not everyone experiences these problems.Improve thumb & grip strength with resistance exercises.Relieve thumb stiffness with hand therapy balls.Regain dexterity with therapeutic putty.Wear a removable wrist support for protection.Use anti-inflammatory gel for pain relief.Bennett’s fracture is confirmed with x-ray views. Pain and swelling limit thumb activities. This is accompanied by rapid swelling in the area of the thumb and wrist, even up towards the elbow. There is severe pain in the region around the base of the thumb. Similarly a soccer goalkeeper can contact the ground with their thumb while attempting to make a save. Trauma through tackling an opponent in rugby and American football can cause a Bennett’s fracture, when there is impact on an outstretched thumb. It is also known as a ‘Boxer’s fracture’, because the mechanism of injury is often a traumatic force going down the length of the first metacarpal bone, where there is a semi bent CMC joint (i.e a punching movement).Īs Dr Bennett can testify, a punch is not the only way this injury occurs.
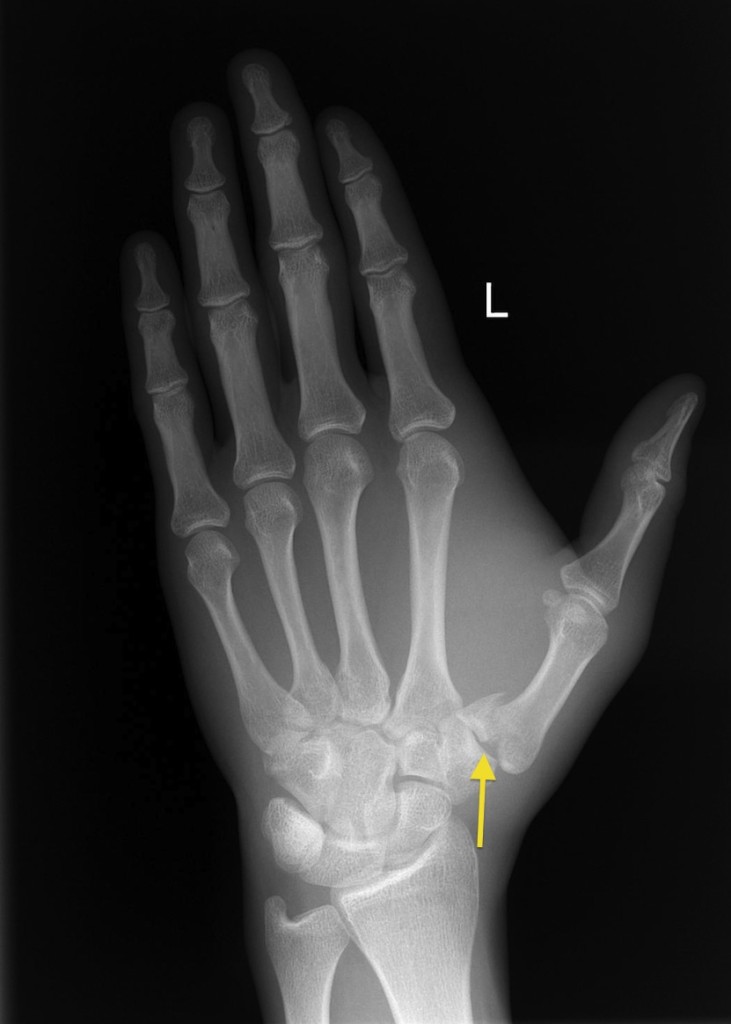
This injury was described by Dr Edward Bennett, who suffered a fracture dislocation of his thumb while horse riding in 1885, and is often referred to as a ‘Bennett’s fracture’. Hence this injury is referred to as a thumb ‘fracture-dislocation’. When a fracture occurs the position of the fracture fragment causes some detachment of the deep ulnar ligament away from the bone, causing a dislocation of the joint. This joint is called the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint, and is normally stabilised by a ligament called the deep ulnar ligament. It refers to a fracture of the metacarpal (thumb) bone at the joint surface with the carpal (wrist) bones. A fracture dislocation at the base of the thumb is not uncommon in boxers, rugby players, American football players and football (soccer) goalkeepers. Bennett’s fracture is a fracture dislocation of the thumb.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
